Abstract
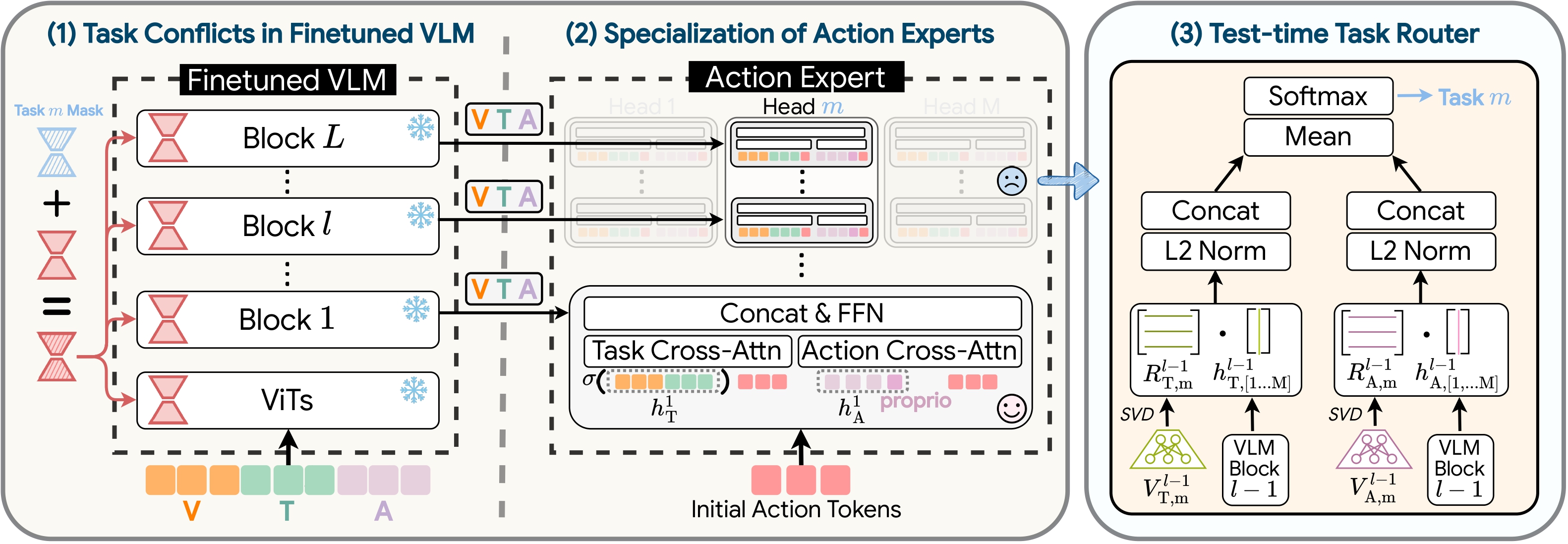
Recent Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models reformulate vision-language models by tuning them with millions of robotic demonstrations. While they perform well when fine-tuned for a single embodiment or task family, extending them to multi-skill settings remains challenging: directly merging VLA experts trained on different tasks results in near-zero success rates. This raises a fundamental question: what prevents VLAs from mastering multiple skills within one model? With an empirical decomposition of learnable parameters during VLA fine-tuning, we identify two key sources of non-mergeability : (1) Finetuning drives LoRA adapters in the VLM backbone toward divergent, task-specific directions beyond the capacity of existing merging methods to unify. (2) Action experts develop inter-block dependencies through self-attention feedback, causing task information to spread across layers and preventing modular recombination. To address these challenges, we present MergeVLA, a merging-oriented VLA architecture that preserves mergeability by design. MergeVLA introduces sparsely activated LoRA adapters via task masks to retain consistent parameters and reduce irreconcilable conflicts in the VLM. Its action expert replaces self-attention with cross-attention-only blocks to keep specialization localized and composable. When the task is unknown, it uses a test-time task router to adaptively select the appropriate task mask and expert head from the initial observation, enabling unsupervised task inference. Across LIBERO, LIBERO-Plus, RoboTwin, and multi-task experiments on the real SO101 robotic arm, MergeVLA achieves performance comparable to or even exceeding individually finetuned experts, demonstrating robust generalization across tasks, embodiments, and environments.
Results
Experiment 1: LIBERO Benchmark
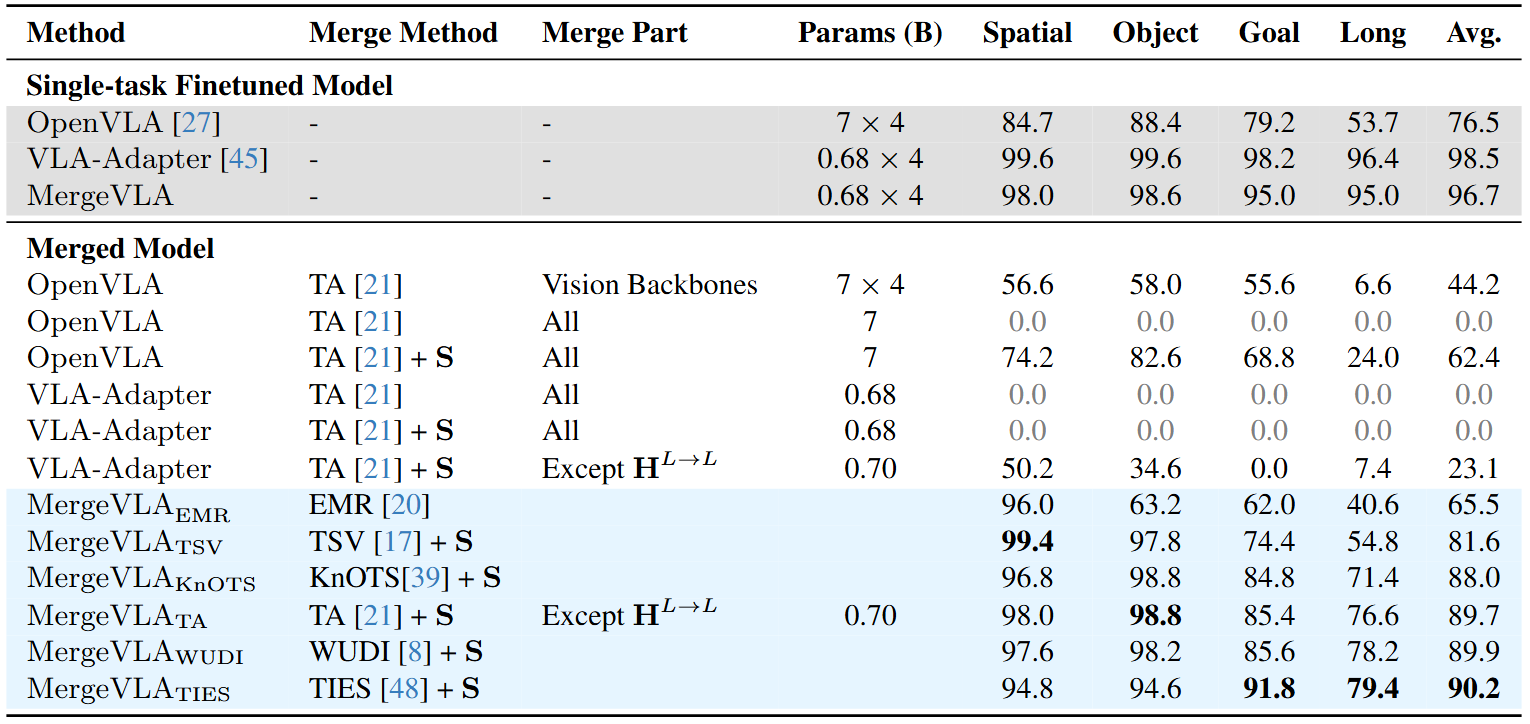
Experiment 2: LIBERO-Plus Benchmark
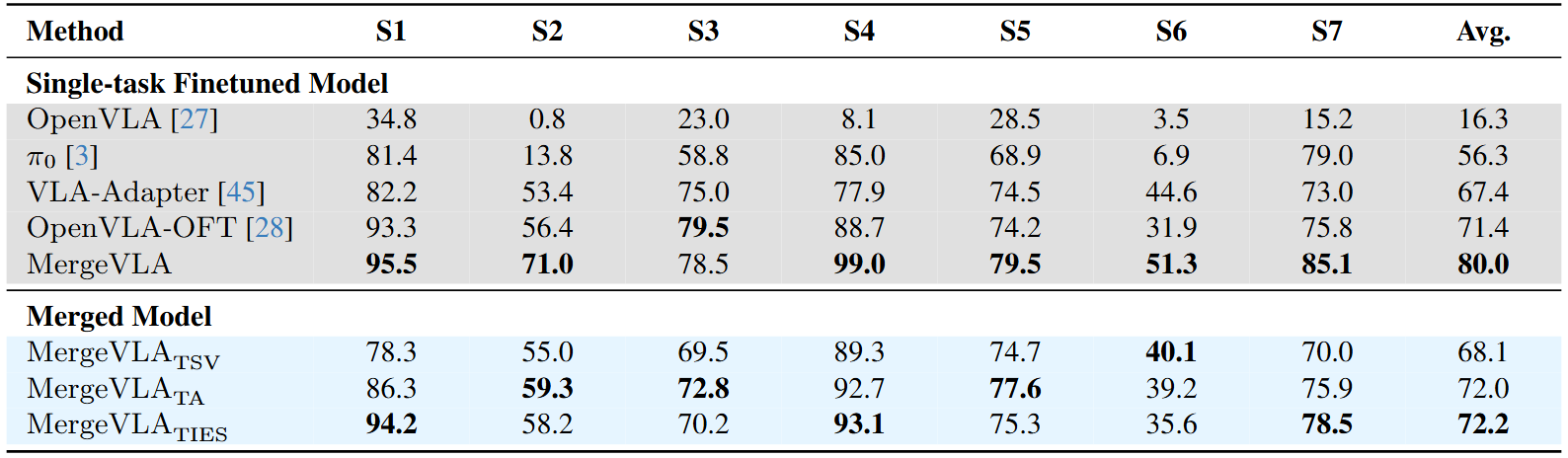
Experiment 3: RoboTwin Benchmark
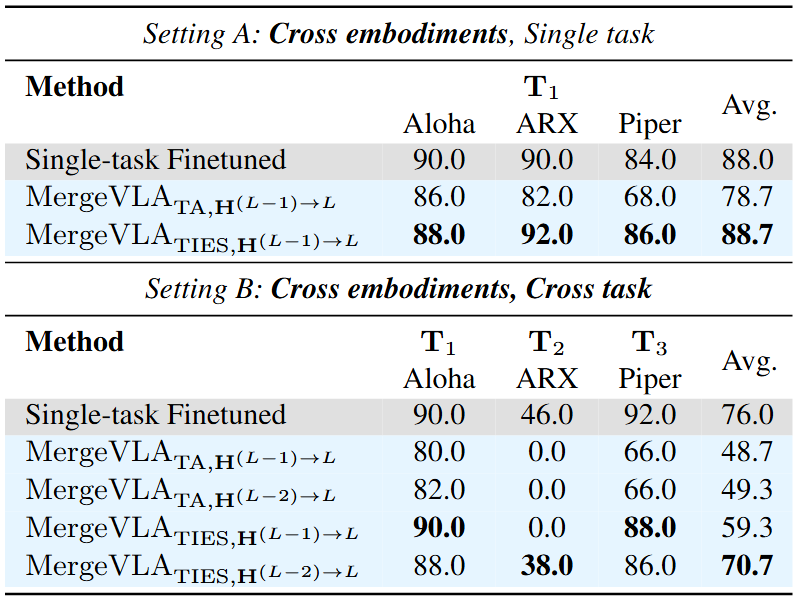
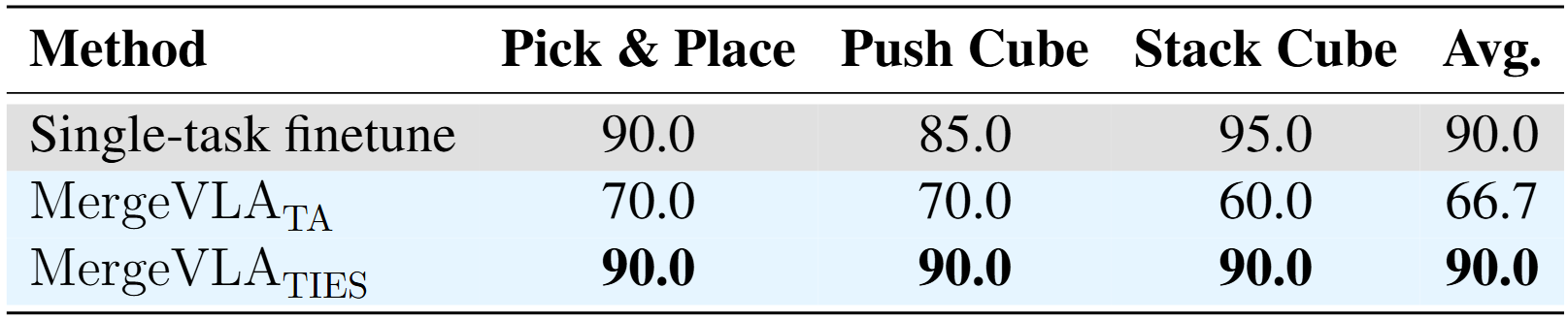
Experiment 4: Real-World Robot
Rollout Videos
LIBERO Benchmark
LIBERO-Plus Benchmark
RoboTwin Benchmark
Real-World Robot Experiments
BibTeX
@misc{fu2025mergevlacrossskillmodelmerging,
title={MergeVLA: Cross-Skill Model Merging Toward a Generalist Vision-Language-Action Agent},
author={Yuxia Fu and Zhizhen Zhang and Yuqi Zhang and Zijian Wang and Zi Huang and Yadan Luo},
year={2025},
eprint={2511.18810},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.RO},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.18810},
}
 : Cross-Skill Model Merging Toward a Generalist Vision-Language-Action Agent
: Cross-Skill Model Merging Toward a Generalist Vision-Language-Action Agent